Updated on July 27th, 2025
Although there’s a very high overlap in principles to optimizing for AI vs traditional search, there are certainly differences due to the changes in retrieval style (single-query match with pages vs Query fan-out and content synthesis), optimization target (page content and metadata vs content chunks and factual spans), results presentation (Ranked list of clickable links vs Synthesized answer, citations, summaries), and success metrics (Rankings, CTR, traffic vs Inclusion/visibility in response, citations/mentions), among other areas, that I highlight here if you’re interested in the shift.
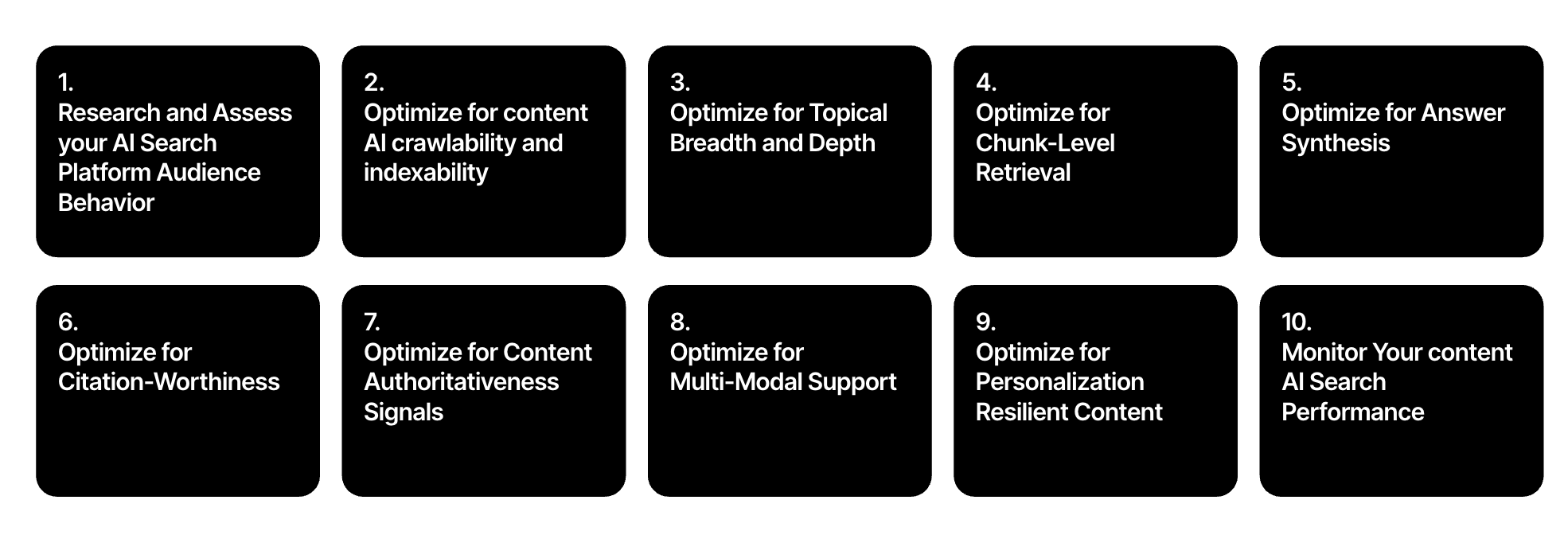
To facilitate actionability, I’ve created a 10 Steps AI Search Content Optimization Checklist, going through the most important aspects to take into account to optimize your content for AI search answers -from chunk optimization, citation worthiness, topical breadth and depth, personalization, etc.-, along with their importance and how to take action, with examples of how to move forward and what to avoid.
Let’s go through it and get access to the Google Sheets version:
1. Research and Assess your AI Search Platform Audience Behavior
Understanding how your audience searches specifically within AI platforms is fundamental due to how AI search behavior differs from traditional search: both in queries purpose, intent, length, as well as engagement/interaction, with long, conversational based, multi-turn queries with high task oriented intent rather than short, keyword based, one-off queries with high navigational intent.
The outcome will allow you to identify the types of questions and topics your content needs to address to appear in AI-generated answers, and how to prioritize based on its current performance vs competitors.
To do:
- Identify the AI Search Platforms Your Audience Uses, the ones already referring top traffic to your site, as well as those referring AI traffic to your competitors
- Identify the most popular and relevant Queries/Prompts used by your audience to search for your product / services and brand across the customer journey
- Identify Your Current Content Performance (mentions, links, sentiment) vs Competitors for relevant Queries/Prompts across the relevant AI Platforms
- Establish your relevant queries/prompts and topics to target and prioritize to optimize for with your content strategy based on your current site and brand performance vs competitors
Example:
✅ Good:
- Use your analytics platform (eg. GA4) to identify the most popular AI search platforms used by your current visitors (ChatGPT, Gemini, Perplexity, etc.)
- Use third-party tools (eg. Similarweb) to identify the most popular AI search platforms referring traffic to competitors
- Identify the most popular prompts referring your site traffic from AI platforms using third-party tools (eg. Similarweb)
- Research the most popular prompts related to your brand and product/service topics in AI platforms (eg. Profound, Sistrix) using your current best performing ones and your top competitors ones as a source
- Assess your site and brand inclusion and visibility (mention, links, sentiment) within the answer for the relevant queries/prompts among the most popular ones (eg. Profound, Peec AI, etc.)
- Identify and assess the inclusion and visibility gap of your own brand vs your top competitors for relevant and popular queries/prompts (eg. Profound, Peec AI, etc.)
- Detect the top queries/prompts and topics to target with your content and to optimize for -and track-, based on current inclusion and visibility vs competitors in most used AI platforms
❌ Bad:
- Ignore referral data from AI sources, failing to track traffic coming from AI platforms like Perplexity or ChatGPT results in missed insights into user behavior and content performance, that you can use to understand your audience preferences and prioritize your efforts.
- Assume users still search in the same way as on traditional Google search without considering how users ask longer, task-based, conversational prompts in AI platforms.
- Fail to analyze your competitors’ AI visibility. Ignoring how your competitors are being cited, linked, or summarized by AI platforms means you miss out on benchmarking, to identify opportunities.
- Only look at branded prompts; focusing solely on prompts mentioning your brand (e.g., “Is [Brand] good?”) while ignoring unbranded products/services topics queries (eg. “Best [product type] for X need”) will limit your content scope and visibility potential.
- Identifying your brand and product/service related mentions for popular prompts, without further assessing the sentiment and links inclusion in them.
- Treat all AI platforms the same, failing to analyze the specific behavior and visibility mechanics of different AI search engines (eg. Google AI Mode vs. ChatGPT) can result in misaligned optimization efforts.
2. Optimize for content AI crawlability and indexability
Relevant content must be accessible, indexable, and reusable by both traditional search engine crawlers and AI-specific agents that retrieve content for large language models and AI-generated answers.
To do:
- Allow search engine crawlers from AI systems through your robots.txt directives in the areas featuring relevant content to surface: GPTBot, Googlebot and Google-Extended token, bingbot, Claude (ClaudeBot/Claude-User/Claude-SearchBot), CCBot, PerplexityBot/Perplexity‑User.
- Avoid blocking AI bots with firewalls or bot filters, by whitelisting their IP ranges.
- Render all essential content server-side or use pre-rendering. Avoid Client Side Rendered JavaScript reliance for key content to avoid indexability challenges as not all AI systems render it.
- Avoid noindexing via meta robots valuable content to be surfaced in AI answers.
- Avoid using a “nosnippet” rule via meta robots in valuable content to be surfaced in AI answers, which will prevent the content from being used as a direct input for AI Overviews and AI Mode.
- Use canonical tags to specify content to be retrieved and used in synthesis from the right pages URLs versions.
- Optimize internal linking to facilitate internal pages crawlability, while using descriptive anchor texts.
Example:
✅ Good:
1. Content You’d Create:
- Title: “Complete Guide to Technical SEO”
- Format: HTML-based pillar page hosted at /technical-seo/, structured with subheadings and linked to supporting cluster pages.
2. Key Crawlability & Indexability Optimizations:
- Allow Key Crawlers in robots.txt: GPTBot, Googlebot, Google-Extended, bingbot, ClaudeBot, CCBot, PerplexityBot.
- AI Bots Whitelisted in Firewall/CDN Rules: Bot traffic (e.g., from GPTBot, PerplexityBot) is allowed and not rate-limited or blocked.
- Server-Side Rendering (SSR): Content is rendered on the server to ensure all bots (including LLMs) can fully access and index it. Avoids JavaScript-heavy frameworks unless pre-rendered.
- No Blocking in Meta Tags: <meta name=”robots” content=”index, follow”>. No use of noindex or nosnippet on high-value informational pages.
- Self-referring Canonical Tags: <link rel=”canonical” href=”https://www.learningseo.io/technical-seo/”>. Avoids duplicate content signals; tells which version to use for synthesis.
- Internal Linking Is Crawlable, and Descriptive: <a href=”/technical-seo/crawlability/” title=”Learn how crawlability impacts SEO”>Crawlability</a>. Clear anchor text helps crawlers understand page context and improve semantic connections.
❌ Bad:
1. Content You’d Create:
- Title: “Technical SEO Tips”
- Format: JavaScript-heavy single-page app at /technical-seo.html that only renders content client-side
2. Critical Crawlability & Indexability Issues:
- Blocked AI Crawlers in robots.txt and firewall
- Client-Side JavaScript Rendering Only: Content loads dynamically via JS with no server-rendered fallback
- Meta Robots Prevent Indexing: <meta name=”robots” content=”noindex, nofollow”>
- Canonicalized Tags: Canonical tag refers to the site root as the original URL version rather than self-canonicalize.
- Poor Internal Linking: Non-crawlable JS based link using vague anchor text like “Click here”
3. Optimize for Topical Breadth and Depth
AI search platforms break complex queries into multiple related subqueries (facets, angles, intents) executed in parallel to retrieve the most relevant content for each aspect (Eg. Query fan-out technique of AI Mode), gathering and synthesizing information from diverse sources. This rewards sites with topical breadth and depth, that feature content that covers each facet in-depth.
To do:
- Query fan-out explores different user intents, so targeting a diversity of angles increases coverage.
- Use a topic cluster model, creating a comprehensive pillar (hub) page for your business, relevant, main broader topics, and cluster pages around specific facets.
- Pillar pages should summarize each topic facet, covering key sections briefly, with links to deeper cluster pages.
- Cluster pages should target specific facets, that should be covered in-depth, ensuring unique purpose and query intent for each page.
- Cross-link between cluster pages where relevant and back to the hub, as a central resource, establishing semantic relationships across content, and helping AI understand the full context and span connections between topics.
Example:
✅ Good:
1. Pillar Page Example:
URL: /technical-seo/
<h1>Technical SEO: A Complete Guide</h1>
<p>Technical SEO involves optimizing your site’s infrastructure to ensure it can be crawled, rendered, and indexed effectively by search engines.</p>
<h2>Core Aspects of Technical SEO</h2>
<ul>
<li><a href=”/technical-seo/crawlability/”>Crawlability</a></li>
<li><a href=”/technical-seo/indexability/”>Indexability</a></li>
<li><a href=”/technical-seo/site-speed/”>Site Speed</a></li>
<li><a href=”/technical-seo/mobile-seo/”>Mobile SEO</a></li>
<li><a href=”/technical-seo/structured-data/”>Structured Data</a></li>
….
</ul>
<p>This guide gives a high-level overview of each component, with links to deep-dive guides that explore each one in detail.</p>
…..
2. Cluster Page Example:
URL: /technical-seo/crawlability/
<h1>What is Crawlability in SEO?</h1>
<p>Crawlability refers to a search engine’s ability to discover and access your website’s content. Barriers like broken links, disallowed URLs in robots.txt, or poor internal linking can prevent effective crawling.</p>
<h2>How to Improve Crawlability</h2>
<ul>
<li>Avoid linking to broken, excessively redirected, or non-canonical URLs.</li>
<li>Use standard <a href> links to ensure crawlers can follow them.</li>
<li>Use descriptive anchor texts in links</li>
…
</ul>
<p>For related concepts, check our guides on <a href=”/technical-seo/indexability/”>Indexability</a> and <a href=”/technical-seo/robots-txt/”>robots.txt</a>.</p>
Why this works:
- Uses hub-and-spoke structure (pillar + clusters)
- Pillar page summarizes facets and links to in-depth resources
- Cluster pages cover specific subtopics thoroughly
- Includes internal links between related cluster pages
- Supports query fan-out by targeting diverse intents under one umbrella
❌ Bad:
<h1>SEO Basics</h1>
<p>SEO includes the optimization of technical configuration, content, and backlinks. Technical SEO is about optimizing the site structure, files like robots.txt, page speed, and mobile-friendliness. It’s important to have a fast site and good architecture.</p>
Why this fails:
- All subtopics are briefly mentioned in a single shallow page
- No dedicated URLs for individual subtopics
- No internal linking to in-depth resources
- Lacks semantic structure to support content relationships
- No cluster model, making it harder to recognize topical authority across related queries
4. Optimize for Chunk-Level Retrieval
AI search engines don’t index or retrieve whole pages; they break content into passages or “chunks” and retrieve the most relevant segments for synthesis. That’s why you should optimize each section like a standalone snippet.
To do:
- Don’t rely on needing the whole page for context, each chunk should be independently understandable.
- Keep passages semantically tight and self-contained.
- One idea per section: keep each passage tightly focused on a single concept.
- Use structured, accessible, and well-formatted HTML with clear subheadings (H2/H3) for every subtopic.
Example:
✅ Good:
<h2>What is Technical SEO?</h2>
<p>Technical SEO focuses on optimizing a website’s infrastructure to ensure search engines can crawl, render, and index content effectively. It includes enhancing internal linking, site speed, mobile usability, and implementing structured data.</p>
Why this works:
- One clear concept: “What is Technical SEO”
- Self-contained and understandable without needing other sections
- Structured with a clear heading and concise explanation
❌ Bad:
<h2>Learn SEO</h2>
<p>SEO covers a lot, like technical SEO, content, link building, and more. For example, technical SEO helps with crawlability and indexation. Content is key for relevance. Link building supports authority. All of these are important parts of an SEO strategy you’ll need to understand eventually as you go through the roadmap…</p>
Why this fails:
- Multiple concepts jammed into one paragraph
- Lacks focus: not semantically tight
- Heading is too broad (“Learn SEO”) and doesn’t guide chunk retrieval
- Requires surrounding context to make sense
5. Optimize for Answer Synthesis
AI search engines synthesize multiple chunks from different sources into a coherent response. This means your content must be easy to extract and logically structured to fit into a multi-source answer.
To do:
- Summarize complex ideas clearly, then expand (A clearly structured “Summary” or “Key takeaways”).
- Start answers with a direct, concise sentence.
- Favor plain, factual, non-promotional tone.
- Use Structured Data to help AI models better classify and extract structured answers.
- Use natural language Q&A format.
Example:
✅ Good:
<h2>What is an SEO audit?</h2>
<p><strong>Summary:</strong> An SEO audit is a comprehensive analysis of a website to identify issues that could affect its optimization and organic visibility in search engines.</p>
<p>It typically includes reviewing the site crawlability, indexability, speed, structured data usage, content relevance and quality, and link popularity vs competitors. The goal is to uncover technical, content and link popularity related issues and opportunities to improve its performance in organic search.</p>
Why this works:
- Starts with a direct, concise summary
- Expands with structured detail
- Uses Q&A format and clear heading
- Plain, factual tone
❌ Bad:
<h2>SEO audits and other essential resources we offer</h2>
<p>At LearningSEO.io, we guide you through audits, checklists, and toolkits tailored to improve your visibility online. Our complete SEO roadmap empowers marketers to become experts. Discover how technical SEO, content, and backlinks can take your traffic to the next level.</p>
Why this fails:
- Promotional and vague language
- No clear definition or summary
- No structured data
- Lacks Q&A structure and extractable format
- Merges multiple topics, hard to synthesize into an AI response
6. Optimize for Citation-Worthiness
AI search engines will cite content when it’s perceived as factually accurate, up-to-date, well-structured, and authoritative. Not every included chunk gets cited – to earn attribution, your content must meet higher trust and clarity criteria.
To do:
- Use specific, up-to-date, verifiable claims, fact-based statements, not vague generalities.
- Include source citations (link to studies, stats, or experts).
- Show authorship and credentials for EEAT signals.
- Use author, organization structured data for brand and entity salience that reinforces citation metadata.
- Refresh key content regularly and signal updated content by adding timestamps.
Example:
✅ Good:
<h2>What is robots.txt and how does it affect SEO?</h2>
<p>The <code>robots.txt</code> file is used to control how search engine crawlers access your website. According to Google Search Central, disallowing a page in <code>robots.txt</code> prevents it from being crawled but does <strong>not</strong> prevent it from being indexed if other signals (like links) point to it. <a href=”https://developers.google.com/search/docs/crawling-indexing/robots/intro”>[Google Search Central, 2025]</a></p>
<p><strong>Updated:</strong> March 2025</p>
<p><strong>Author:</strong> Aleyda Solis, SEO Consultant and Author, LearningSEO.io</p>
Why this works:
- Uses a precise, verifiable claim directly linked to official documentation
- Clarifies a common SEO misconception with factual accuracy
- Shows authorship and role for EEAT
- Fresh update date
❌ Bad:
<h2>robots.txt Explained</h2>
<p>robots.txt is important for SEO. You can use it to stop Google from indexing your pages. It’s a powerful tool and should be used carefully.</p>
Why this fails:
- Inaccurate and misleading: robots.txt blocks crawling, not necessarily indexing
- No source or external reference
- Vague, generalized language
- No authorship, timestamp, or structured data for citation relevance
7. Optimize for Content Authoritativeness Signals
Authority increases the likelihood that your content will be included and cited in AI-generated answers, especially as these systems rely on entity recognition and reputation to determine which sources to trust. Without clear authority signals -such as expert bylines, structured data, external citations, and mentions on reputable sites- your content is less likely to be surfaced, even if it’s accurate.
To do:
- Optimize your brand presence across web platforms, including social channels, in a consistent way, linking back to your main site, engaging with your community, answering reviews, etc.
- Publish original research, reports, or data studies, conduct surveys, compile unique datasets, or run industry studies. Promote them to journalists and bloggers who create content roundups.
- Secure coverage in industry and expert publications, contribute quotes or guest content to respected newsletters and blogs in your industry.
- Promote your content across relevant third-party channels: Engage with influencers, experts, Slack groups, subreddits, and communities. Ask for feedback and mentions.
Example:
✅ Good:
1. Content You’d Create:
- Title: “2025 State of SEO Tools: Usage Trends by Role, Region & Experience”
- Type: Original research study with downloadable dataset + visualizations
- Format: Long-form report + CSV + embeddable charts
- Topic Cluster Target: SEO tools → fits under broader topical authority of SEO fundamentals
Main Characteristics:
- Based on a survey of 1,000+ SEO professionals from multiple regions and experience levels
- Covers detailed breakdowns by tool category (crawlers, keyword research, rank trackers, AI SEO tools, etc.)
- Includes original charts, graphs, and data visualizations (served as HTML, not just images)
- Authored by a known SEO expert (with byline, profile, and social links)
- Structured data includes author, organization, datePublished, sameAs for brand and person
- Timestamped and refreshed yearly, showing commitment to accuracy and timeliness
- Links to external references (e.g., comparisons to 2024 reports from Semrush, Ahrefs, or Google)
2. How You’d Secure Coverage & Promotion:
- Direct outreach to publications like SEJ, SEL, SER offering exclusive preview or quote angles with data points by region/tool category for coverage
- Pitch to industry newsletters like SEOFOMO, Core Updates, SEO for Lunch or Growth Memo, covering the latest trends, to include the research in the next edition, offering a blurb
- Submission of the research to SEO News aggregators like SEOFOMO News
- Share the research with your audience on social platforms (LinkedIn, X, Bluesky) by teasing standout stats
- Republish a research summary and top insights in a LinkedIn post linking to the main research to learn more
- Post in SEO Slack communities and subreddit threads with clear value + charts
- Ask SEO specialists to contribute commentary, include 3–4 short quotes from respected SEO professionals in the report. This encourages co-promotion and enhances perceived authority.
Why This Works:
- It’s Original, Primary-Source Content
- It Has Clear EEAT (Expertise, Experience, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness) Signals
- It’s Promoted and Cited Externally
- It’s Structured for Extraction and Synthesis
- It’s Refreshed and Timestamped
❌ Bad:
1. Content You’d Create:
- Title: “Top SEO Tools for 2025”
- Type: Blog post with affiliate links
- Format: Listicle-style with shallow descriptions
Why It Lacks Authority:
- No original data, quotes, or insights – repackaged info from others
- Written under a generic “Team” byline with no author profile or structured metadata
- Includes promotional CTAs, affiliate links, and vague pros/cons
- No citations to credible external sources or comparisons over time
- No links from or mentions on trusted SEO or marketing publications
- No engagement across social, email, or trusted communities
- Not updated or timestamped; no relevance signal for AI systems
8. Optimize for Multi-Modal Support
AI search systems are increasingly retrieving and synthesizing multimodal content, -including images, charts, tables, videos-, to better answer user queries, giving opportunity to provide more useful, scannable and engaging answers for users.
To do:
- Ensure images and videos crawlability for search and AI bots.
- Serve images via clean HTML and avoid lazy-loading with JS-only rendering, since LLM-based scrapers may not render JS-heavy elements.
- Images should use descriptive alt text that includes topic context.
- Add captions to images and videos with explanation right below or beside the visual.
- Use <figure>, <table>, etc. with contextually correct markup to help parse tables, figures, lists.
- Avoid images of tables, use HTML tables instead for a machine-readable format supporting tokenization and summarization.
Example:
✅ Good:
<h2>SEO Audit Process Overview</h2>
<p>An SEO audit evaluates key website configuration areas like crawlability, indexability, content quality, site speed, and backlinks.</p>
<figure>
<img src=”/images/seo-audit-process.png” alt=”SEO audit process flowchart: crawlability, indexability, content, speed, backlinks” />
<figcaption>Figure 1: SEO audit flow showing the five core focus areas reviewed during a technical SEO audit.</figcaption>
</figure>
<h3>SEO Audit Focus Areas</h3>
<table>
<thead>
<tr>
<th>Area</th>
<th>What It Includes</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr>
<td>Crawlability</td>
<td>robots.txt, sitemap, internal linking</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Indexability</td>
<td>Canonical tags, noindex, HTTP status codes</td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
Why this works:
- Uses <figure> and <figcaption> for machine-readable image context
- Alt text is descriptive and relevant to the topic
- Uses a real HTML table -not an image- allowing AI models to tokenize and summarize content
- Visual content is inline and crawlable, no JavaScript-dependence
- Enhances scannability and multimodal retrieval for AI search synthesis
❌ Bad:
<h2>SEO Audit Overview</h2>
<p>The SEO audit is shown below:</p>
<img src=”/images/audit-summary.jpg” />
<p>Here’s the table:</p>
<img src=”/images/audit-checklist.jpg” />
Why this fails:
- Images are uncaptioned, providing no surrounding context
- Alt text is missing or unclear (assuming <img> has no proper alt)
- Table is shown as an image – not machine-readable, no semantic structure
- No use of semantic elements like <figure> or <table>
- May rely on JavaScript lazy-loading, blocking LLM-based crawlers from retrieving content
9. Optimize for Personalization Resilient Content
AI search engines can personalize answers using a combination of contextual signals, retrieval techniques, and user-centric data: User location, user intent, search history or session context, entity familiarity or brand bias via user patterns, user feedback and engagement.
To do:
- Cover multiple intents for the same topic, so your content aligns with many personalized subqueries, increasing surface area.
- Optimize for localized intent by including regional content, currencies, addresses, or local schema markup (Place, LocalBusiness).
- Add contextual signals that aligns content with profile-based personalization, segmenting content for specific personas or use cases.
- Get links and mentions across reputable domains and popular platforms where your audience engages via digital PR, contributor posts, Wikipedia citations, mentions in research, strong community and social media presence and engagement, since AI search may personalized towards brands or sites the user previously interacted with or that have high entity recognition for a given topic.
- Retain attention and engagement with fast, useful content that gives a satisfying user experience since AI search systems refine results based on user behavior, thumbs up/down, etc. This feedback loops into ranking and synthesis decisions for future answers.
Example:
✅ Good:
1. Content You’d Create:
- Title: “SEO Learning Paths for Different Roles: Freelancers, In-House Teams, and Beginners”
- Format: Interactive hub page with role-based navigation + region-specific details
2. Main Characteristics:
- Multi-Intent Coverage
- Sections for: How to learn SEO, Best SEO courses for freelancers, In-house SEO training, Free vs paid options
- Each with its own heading, structured content, and internal links
- Localized Elements
- Country-specific training examples
- Marked up with LocalBusiness, Place, and geo-specific schema
- Persona-Based Segmentation
- “Freelancers” section highlights flexible, low-cost options
- “In-house” section focuses on collaboration and documentation workflows
- “Career changers” section includes entry-level course paths and certification prep
- Entity Familiarity & Distribution
- Authored by a known expert with structured byline (author schema)
- Cited in newsletters like SEOFOMO, Core Updates and SEOForLunch
- Shared in SEO Reddit threads, Slack groups, and digital marketing LinkedIn posts
- UX & Engagement Signals
- Fast, responsive design
- Includes a quiz: “Which SEO path fits you?” → boosts session duration
- Social share buttons and feedback widgets (“Was this helpful?”)
Why this works:
It matches multiple intents, adapts to different personas and locations, builds entity authority, and generates positive user engagement signals – making it highly resilient in personalized AI-driven search environments.
❌ Bad:
Content You’d Create:
- Title: “Our SEO Course: Learn in 30 Days”
- Format: One generic landing page promoting a single product
Why This Fails:
- Single Intent Targeted: Focuses only on “buy SEO course” – ignores informational, comparative, or persona-driven intents.
- No Localization: No region-specific details or markup. Doesn’t serve localized queries or international search needs.
- Doesn’t distinguish between audiences: beginners, pros, freelancers, or agencies. No use of personas, segmentation, or contextual cues
- Weak Authority & Engagement: No expert author, no citations, no community validation. Not mentioned or shared outside owned channels. Slow to load and lacks interactive elements.
10. Monitor Your content AI Search Performance
Monitoring your brand content visibility, sentiment, referrals from relevant AI answers allows you to identify opportunities to improve inclusions in AI-generated answers, and strengthen your presence in AI search responses vs competitors.
To do:
- Track the most popular prompts used by your audience to look for your product, services and brand in AI platforms.
- Track and evaluate your brand mentions from AI search answers for relevant product/service related, as well as brand focused prompts across AI search platforms.
- Monitor and assess the sentiment of your brand mentions in AI search answers for relevant product/service, as well as brand focused prompts across AI search platforms.
- Monitor the inclusion of links to your Website from relevant brand mentions in AI search answers across platforms.
- Benchmark your brand mentions, sentiment and links in relevant answers vs main competitors across AI search platforms.
- Benchmark your brand mentions, sentiment and links inclusions in AI answers content sources vs main competitors across AI search platforms.
- Monitor AI referral traffic via your analytics platform by creating a new channel for AI platforms sources to understand its growth over time, pages destinations, engagement, and conversion.
- Monitor the crawling behavior of AI platforms on your site: Crawl frequency, crawled URLs and depth, HTTP status codes returned, robots.txt access patterns, requested content type, changes in crawl behavior over time, etc.
Example:
✅ Good:
- Monitor popular prompts related to your brand and main product/service topics in AI tools that provide them (eg. Profound, Similarweb, Sistrix, etc.) to understand your audience’s AI search behavior and use this data to inform your content optimization strategy.
- Track your brand mentions, sentiment, and links in AI answers separately for each major AI search platform (eg. ChatGPT, Gemini, AI Overviews/AI Mode, Perplexity, etc.).
- Check the sources cited in relevant AI answers, especially those where your brand is not mentioned, to identify new citation opportunities.
- Assess the sentiment of your brand mentions in AI answers compared to competitors, to uncover reputation management needs and positioning gaps.
- Monitor AI driven traffic behavior (eg. visited pages, engagement, and conversion) versus traditional search traffic to understand behavioral differences and identify optimization opportunities.
- Monitor AI bots’ crawling behavior: crawl frequency, crawled URLs and depth, HTTP status codes returned, robots.txt access patterns, requested content types, and changes in crawl behavior over time, to ensure your key content is effectively accessed and indexed.
❌ Bad:
- Assuming your users’ behavior and queries in AI search platforms are the same as in traditional search engines, without analyzing AI specific prompt data.
- Monitoring your brand mentions, sentiment, and links in only one AI platform (eg. ChatGPT) and assuming results are the same across all others.
- Ignoring content sources in AI answers and focusing only on surface level answer metrics.
- Monitoring brand mentions in AI answers but neglecting to analyze sentiment or context.
- Not segmenting or analyzing AI-driven traffic, and assuming it behaves the same as traditional search traffic.
- Failing to monitor AI bots’ crawling behavior and assuming it is identical to that of traditional search engine crawlers.
Top sources and more information about AI search content optimization:
- Engineering Relevant Content: Tips to Get Your Content into LLMs by Francine Monahan
- How AI Mode Works and How SEO Can Prepare for the Future of Search by Mike King
- Chunked, Retrieved, Synthesized – Not Crawled, Indexed, Ranked by Duane Forrester
- Writing and optimizing content for NLP-Driven SEO by Jan-Willem Bobbink
- How Content Structure Matters for AI Search by Chris Green
- Revisiting ‘useful content’ in the age of AI-dominated search by Amanda King
- Query Fan-Out: A Data-Driven Approach to AI Search Visibility by Andrea Volpini
- What does Google’s AI Mode really want from your product page – and what exactly is Chunk Optimization? by Andrea Volpini
Find these and more resources in LearningAIsearch.com, a free roadmap to learn AI search optimization.
Get the AI Search Content Optimization Checklist in Google Sheets
Start using the AI Search Content Optimization Checklist by copying it from Google Sheets here.
Use The AI Search Content Optimizer GPT
If you want to automate the process, I’ve created a GPT based on the checklist to help you accelerate your content optimization process. Check the The AI Search Content Optimizer GPT.